Describe the Anatomy of the Eye and Its Accessory Structures
Numerous hairs project obliquely from the surface of the skin. Accessory Structures of the Eye.

Accessory Clinical Anatomy Operative Surgery Facebook
The accessory visual structures are the protecting and supporting structures of the eye including the eyebrow eyelids and lacrimal apparatus.

. Eye Anatomy and Physiology. It perceives the light energy converts it into electrical energy thereby helping us to see. The inside of the eye contains the two refractive structures of the eye called the lens and vitreous body.
Thick fold of connective tissue that gives form and support to the eyelids. Eyelashes - Hairs growing at the edge of the eyelid which are very sensitive tactile receptors. Discuss how the retina converts this image to nerve signals.
Eyelids eyelashes eyebrows lacrimal apparatus extrinsic eye muscles. Eyebrows eyelids conjunctiva lacrimal apparatus and extrinsic eye muscles. External components include structures which can be seen on the exterior of the eye and internal components include structures present within.
When you have completed this section you should be able to describe the anatomy of the eye and its accessory structures. The accessory organs of the eye include the ocular muscles the fasciæ the eyebrows the eyelids the conjunctiva and the lacrimal apparatus. Structure and Function.
The cornea is the clear outer part of the eyes focusing system located at the front of the eye. Eyebrows eyelids conjunctiva lacrimal apparatus and extrinsic eye muscles. The remaining fibrous network and vasculature.
Accessory Structures of the Eye Just like in other units of this lab manual we discuss eye components as they relate to one eye even though we have two eyes. Eyelids - 4 layers of tissue theyre actually the thinnest tissue in the body. An eye is the sense organ of vision.
The lens is a clear part of the eye behind the iris that helps to. Hence it does not possess a perfect spherical shape. Describe the structure and function of the layers of the eye the lens and the humors of the eye.
Explain why different types of receptor cells and neural circuits are. These include the eyebrows the eyelids and eyelashes the conjunctiva and the lacrimal apparatus. Structurae bulbi accessoriae are responsible for the movement of the eyeball and its protectionThe accessory structures are.
Describe the anatomy and function of the accessory structures of the eye including. The ocular muscles are the. The eyelids are divided into an orbital and a tarsal part.
A P name for the eyelids. Anatomically the eye comprises two components fused into one. The epithelium of the cornea and lens are derived from the surface ectodermThe endothelium of the cornea sclera and choroid arise from the neural crest cellsThe neuroectoderm produces the posterior part of the iris optic nerve and retina.
Functions of the Accessory Structures of the Eye. There are three major parts in each eye like. Here are descriptions of some of the main parts of the eye.
The division is done by the superior palpebral sulcus. Describe the structure and function of the layers of the eye the lens and the humors of the eye. Embryology of the eye The eyes are formed from several embryonic layers.
There are seven accessory organs of the eye all with varying functions. Trace the pathway of nerve impulses from the retina to the cerebral. The sclera fibrous layer Choroid layer.
The role of refractive structures to bend the direction of the light that falls onto the eye and focus it onto the retina. Discuss the structure of the retina and its receptor cells. The adnexal structures also help to keep the cornea.
The eyebrows eyelids eyelashes lacrimal gland and drainage apparatus all play a crucial role with regards to globe protection lubrication and minimizing the risk of ocular infection. Together with the cornea and aqueous humor the vitreous body and lens belong to the refractive media of the eyeball. The Ocular Muscles musculi oculi.
Eyebrows - Catch sweat or debris coming off the forehead into the eye. These are two arched eminences of skin surmounting the supraorbital margins of the frontal bone. Describe the anatomy of the eye its accessory structures discuss the structure of the retina its receptor cells forms from a cup-shaped outgrowth of the optic vesicle nerve fibers all lead to optic disc to form bundle and travel down optic nerve.
Describe the anatomy and function of the accessory structures of the eye including. The Accessory Structures of the Eye. The eye has many accessory structures including the conjunctiva lacrimal gland lacrimal sac.
Eyes are spheroid shape organs fitted into the two orbitals of the skull. The accessory structures of the eye include the eyelids eyelashes eyebrows the lacrimal apparatus and extrinsic eye muscles. Name the 5 accessory structures of the eye.
The iris is the colored part of the eye that regulates the amount of light entering the eye. Accessory structures of the eye Latin. Explain how the optical system of the eye creates an image on the retina.

Eye Structure Function Ppt Download

Accessory Structures Of The Eye And Structural Components Of The Eye Flashcards Quizlet
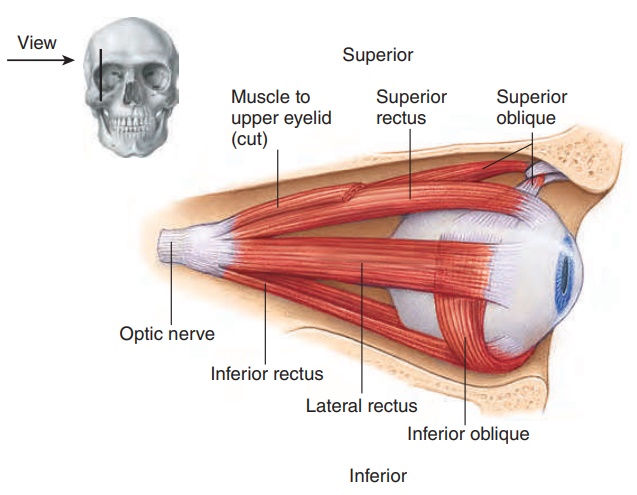
Accessory Structures Of The Eye
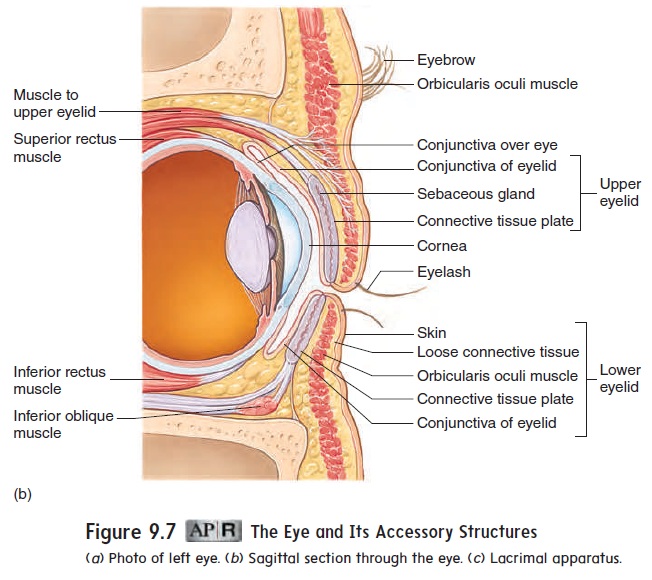
Accessory Structures Of The Eye

Accessory Structures Of Eye Ppt Download

External Anatomy Of The Eye And Surrounding Accessory Structures A Photo Of Anterior View Of The Eye And Accessory Struc Anatomy Eyes Anatomy And Physiology

The Eye Human Anatomy Quiz Quizizz
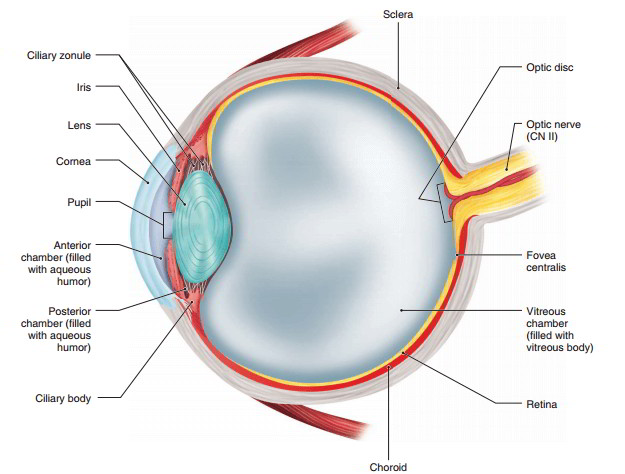
The Structure Of The Eye And The Functions Of These Accessory Structures Earth S Lab
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Describe the Anatomy of the Eye and Its Accessory Structures"
Posting Komentar